Search K
Appearance
Appearance
Other ways to support HackTricks:
.SFw_cIWc.png)
Use Trickest to easily build and automate workflows powered by the world's most advanced community tools.
Get Access Today:
The Docker engine employs the Linux kernel's Namespaces and Cgroups to isolate containers, offering a basic layer of security. Additional protection is provided through Capabilities dropping, Seccomp, and SELinux/AppArmor, enhancing container isolation. An auth plugin can further restrict user actions.
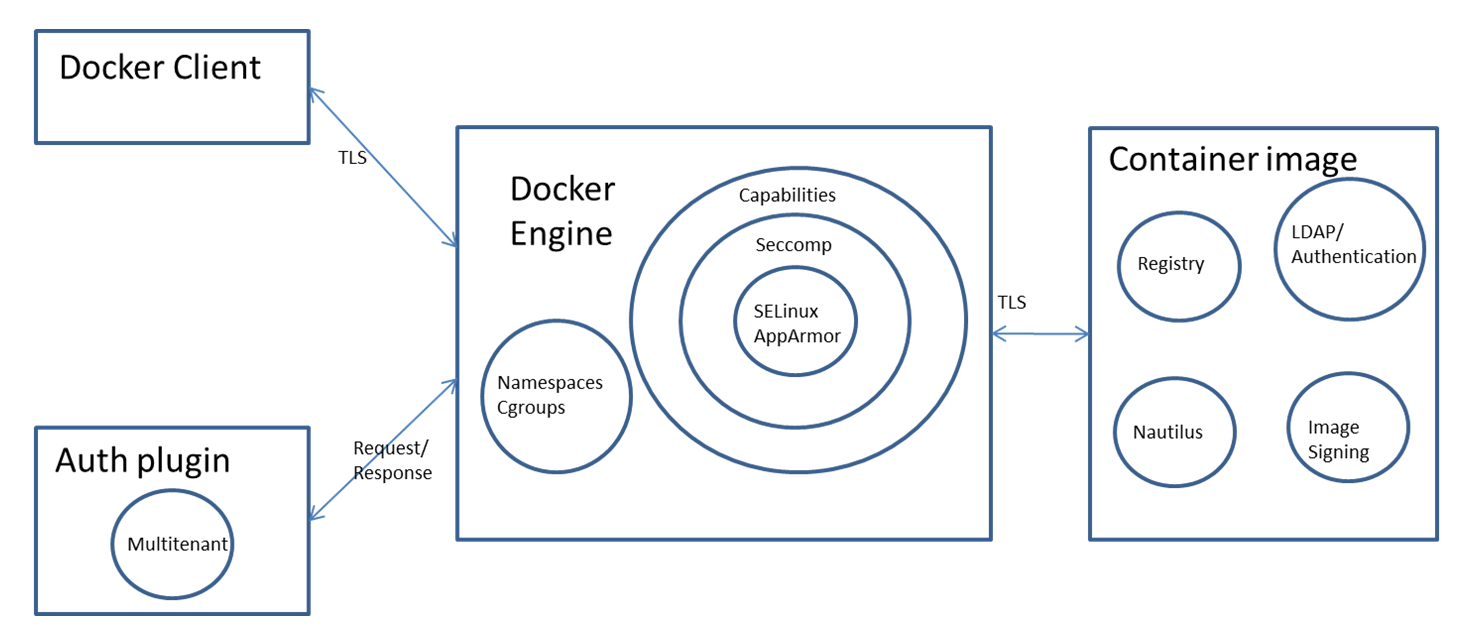
The Docker engine can be accessed either locally via a Unix socket or remotely using HTTP. For remote access, it's essential to employ HTTPS and TLS to ensure confidentiality, integrity, and authentication.
The Docker engine, by default, listens on the Unix socket at unix:///var/run/docker.sock. On Ubuntu systems, Docker's startup options are defined in /etc/default/docker. To enable remote access to the Docker API and client, expose the Docker daemon over an HTTP socket by adding the following settings:
DOCKER_OPTS="-D -H unix:///var/run/docker.sock -H tcp://192.168.56.101:2376"
sudo service docker restartHowever, exposing the Docker daemon over HTTP is not recommended due to security concerns. It's advisable to secure connections using HTTPS. There are two main approaches to securing the connection:
Certificates are utilized to confirm a server's identity. For detailed examples of both methods, refer to this guide.
Container images can be stored in either private or public repositories. Docker offers several storage options for container images:
Containers can have security vulnerabilities either because of the base image or because of the software installed on top of the base image. Docker is working on a project called Nautilus that does security scan of Containers and lists the vulnerabilities. Nautilus works by comparing the each Container image layer with vulnerability repository to identify security holes.
For more information read this.
docker scanThe docker scan command allows you to scan existing Docker images using the image name or ID. For example, run the following command to scan the hello-world image:
docker scan hello-world
Testing hello-world...
Organization: docker-desktop-test
Package manager: linux
Project name: docker-image|hello-world
Docker image: hello-world
Licenses: enabled
✓ Tested 0 dependencies for known issues, no vulnerable paths found.
Note that we do not currently have vulnerability data for your image.trivy -q -f json <container_name>:<tag>snyk container test <image> --json-file-output=<output file> --severity-threshold=highclair-scanner -w example-alpine.yaml --ip YOUR_LOCAL_IP alpine:3.5Docker image signing ensures the security and integrity of images used in containers. Here's a condensed explanation:
export DOCKER_CONTENT_TRUST=1. This feature is off by default in Docker version 1.10 and later.To back up your private keys, use the command:
tar -zcvf private_keys_backup.tar.gz ~/.docker/trust/privateWhen switching Docker hosts, it's necessary to move the root and repository keys to maintain operations.
.SFw_cIWc.png)
Use Trickest to easily build and automate workflows powered by the world's most advanced community tools.
Get Access Today:
Main Process Isolation Features
In containerized environments, isolating projects and their processes is paramount for security and resource management. Here's a simplified explanation of key concepts:
Namespaces
unshare: The unshare command (or the underlying syscall) is utilized to create new namespaces, providing an added layer of isolation. However, while Kubernetes doesn't inherently block this, Docker does./proc directory, using nsenter for entry.Control Groups (CGroups)
release_agent feature, which, if misconfigured, could potentially be exploited for unauthorized access.Capability Drop
These are the remaining capabilities after the process drop the others:
Current: cap_chown,cap_dac_override,cap_fowner,cap_fsetid,cap_kill,cap_setgid,cap_setuid,cap_setpcap,cap_net_bind_service,cap_net_raw,cap_sys_chroot,cap_mknod,cap_audit_write,cap_setfcap=epSeccomp
It's enabled by default in Docker. It helps to limit even more the syscalls that the process can call.
The default Docker Seccomp profile can be found in https://github.com/moby/moby/blob/master/profiles/seccomp/default.json
AppArmor
Docker has a template that you can activate: https://github.com/moby/moby/tree/master/profiles/apparmor
This will allow to reduce capabilities, syscalls, access to files and folders...
Namespaces are a feature of the Linux kernel that partitions kernel resources such that one set of processes sees one set of resources while another set of processes sees a different set of resources. The feature works by having the same namespace for a set of resources and processes, but those namespaces refer to distinct resources. Resources may exist in multiple spaces.
Docker makes use of the following Linux kernel Namespaces to achieve Container isolation:
For more information about the namespaces check the following page:
Linux kernel feature cgroups provides capability to restrict resources like cpu, memory, io, network bandwidth among a set of processes. Docker allows to create Containers using cgroup feature which allows for resource control for the specific Container.
Following is a Container created with user space memory limited to 500m, kernel memory limited to 50m, cpu share to 512, blkioweight to 400. CPU share is a ratio that controls Container’s CPU usage. It has a default value of 1024 and range between 0 and 1024. If three Containers have the same CPU share of 1024, each Container can take upto 33% of CPU in case of CPU resource contention. blkio-weight is a ratio that controls Container’s IO. It has a default value of 500 and range between 10 and 1000.
docker run -it -m 500M --kernel-memory 50M --cpu-shares 512 --blkio-weight 400 --name ubuntu1 ubuntu bashTo get the cgroup of a container you can do:
docker run -dt --rm denial sleep 1234 #Run a large sleep inside a Debian container
ps -ef | grep 1234 #Get info about the sleep process
ls -l /proc/<PID>/ns #Get the Group and the namespaces (some may be uniq to the hosts and some may be shred with it)For more information check:
Capabilities allow finer control for the capabilities that can be allowed for root user. Docker uses the Linux kernel capability feature to limit the operations that can be done inside a Container irrespective of the type of user.
When a docker container is run, the process drops sensitive capabilities that the proccess could use to escape from the isolation. This try to assure that the proccess won't be able to perform sensitive actions and escape:
This is a security feature that allows Docker to limit the syscalls that can be used inside the container:
AppArmor is a kernel enhancement to confine containers to a limited set of resources with per-program profiles.:
container_t.container_file_t.container_t label can only interact (read, write, execute) with files labeled as container_file_t.This mechanism ensures that even if a process within a container is compromised, it's confined to interacting only with objects that have the corresponding labels, significantly limiting the potential damage from such compromises.
In Docker, an authorization plugin plays a crucial role in security by deciding whether to allow or block requests to the Docker daemon. This decision is made by examining two key contexts:
These contexts help ensure that only legitimate requests from authenticated users are processed, enhancing the security of Docker operations.
If you are not properly limiting the resources a container can use, a compromised container could DoS the host where it's running.
# stress-ng
sudo apt-get install -y stress-ng && stress-ng --vm 1 --vm-bytes 1G --verify -t 5m
# While loop
docker run -d --name malicious-container -c 512 busybox sh -c 'while true; do :; done'nc -lvp 4444 >/dev/null & while true; do cat /dev/urandom | nc <target IP> 4444; doneIn the following page you can learn what does the --privileged flag imply:
If you are running a container where an attacker manages to get access as a low privilege user. If you have a miss-configured suid binary, the attacker may abuse it and escalate privileges inside the container. Which, may allow him to escape from it.
Running the container with the no-new-privileges option enabled will prevent this kind of privilege escalation.
docker run -it --security-opt=no-new-privileges:true nonewpriv#You can manually add/drop capabilities with
--cap-add
--cap-drop
# You can manually disable seccomp in docker with
--security-opt seccomp=unconfined
# You can manually disable seccomp in docker with
--security-opt apparmor=unconfined
# You can manually disable selinux in docker with
--security-opt label:disableFor more --security-opt options check: https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/run/#security-configuration
It's crucial to avoid embedding secrets directly in Docker images or using environment variables, as these methods expose your sensitive information to anyone with access to the container through commands like docker inspect or exec.
Docker volumes are a safer alternative, recommended for accessing sensitive information. They can be utilized as a temporary filesystem in memory, mitigating the risks associated with docker inspect and logging. However, root users and those with exec access to the container might still access the secrets.
Docker secrets offer an even more secure method for handling sensitive information. For instances requiring secrets during the image build phase, BuildKit presents an efficient solution with support for build-time secrets, enhancing build speed and providing additional features.
To leverage BuildKit, it can be activated in three ways:
export DOCKER_BUILDKIT=1DOCKER_BUILDKIT=1 docker build .{ "features": { "buildkit": true } }, followed by a Docker restart.BuildKit allows for the use of build-time secrets with the --secret option, ensuring these secrets are not included in the image build cache or the final image, using a command like:
docker build --secret my_key=my_value ,src=path/to/my_secret_file .For secrets needed in a running container, Docker Compose and Kubernetes offer robust solutions. Docker Compose utilizes a secrets key in the service definition for specifying secret files, as shown in a docker-compose.yml example:
version: "3.7"
services:
my_service:
image: centos:7
entrypoint: "cat /run/secrets/my_secret"
secrets:
- my_secret
secrets:
my_secret:
file: ./my_secret_file.txtThis configuration allows for the use of secrets when starting services with Docker Compose.
In Kubernetes environments, secrets are natively supported and can be further managed with tools like Helm-Secrets. Kubernetes' Role Based Access Controls (RBAC) enhances secret management security, similar to Docker Enterprise.
gVisor is an application kernel, written in Go, that implements a substantial portion of the Linux system surface. It includes an Open Container Initiative (OCI) runtime called runsc that provides an isolation boundary between the application and the host kernel. The runsc runtime integrates with Docker and Kubernetes, making it simple to run sandboxed containers.
Kata Containers is an open source community working to build a secure container runtime with lightweight virtual machines that feel and perform like containers, but provide stronger workload isolation using hardware virtualization technology as a second layer of defense.
--privileged flag or mount a Docker socket inside the container. The docker socket allows for spawning containers, so it is an easy way to take full control of the host, for example, by running another container with the --privileged flag.--cap-drop=all) and enable only those that are required (--cap-add=...). Many of workloads don’t need any capabilities and adding them increases the scope of a potential attack.If you are inside a docker container or you have access to a user in the docker group, you could try to escape and escalate privileges:
If you have access to the docker socket or have access to a user in the docker group but your actions are being limited by a docker auth plugin, check if you can bypass it:
.SFw_cIWc.png)
Use Trickest to easily build and automate workflows powered by the world's most advanced community tools.
Get Access Today:
Other ways to support HackTricks: